SpaceX Starship Test Fails Mid-Flight: USD-Backed Program Faces New Engineering Hurdles
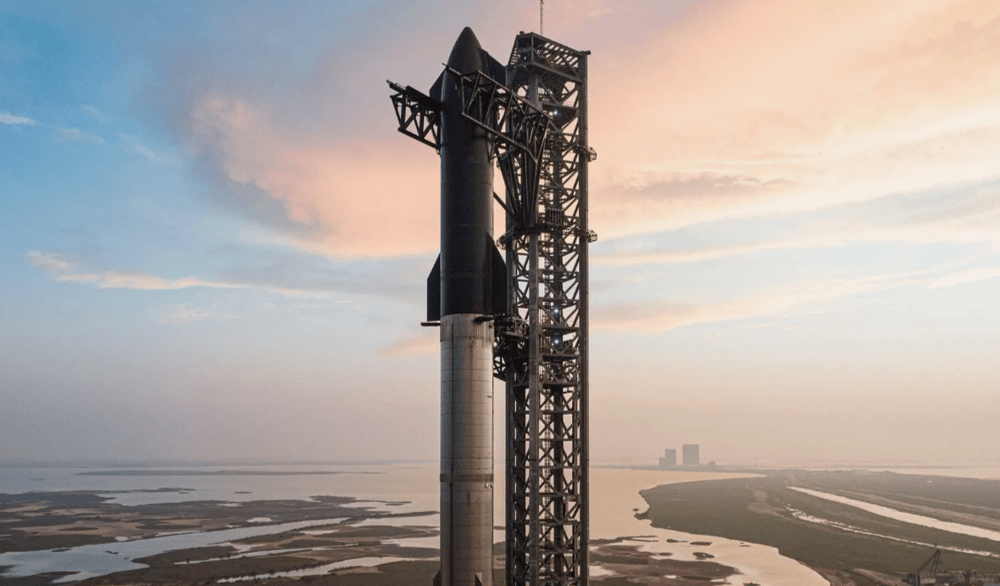
On Tuesday, SpaceX launched its most powerful spacecraft, the 400-foot Starship, from its Texas Starbase. The launch, designed as a critical test of Elon Musk’s Mars exploration architecture, ended prematurely after the rocket lost control mid-flight. While the rocket surpassed the altitude achieved by previous failed tests earlier this year, it did not reach its most ambitious testing milestones.
The aborted mission highlights the complex engineering and regulatory challenges that continue to confront SpaceX as it develops the vehicle meant to carry humans to Mars. Funded primarily through private capital and supported by lucrative U.S. government contracts in USD, the Starship project remains a linchpin of Musk’s long-term aerospace strategy.
Test Results, Implications, and Programmatic Risks
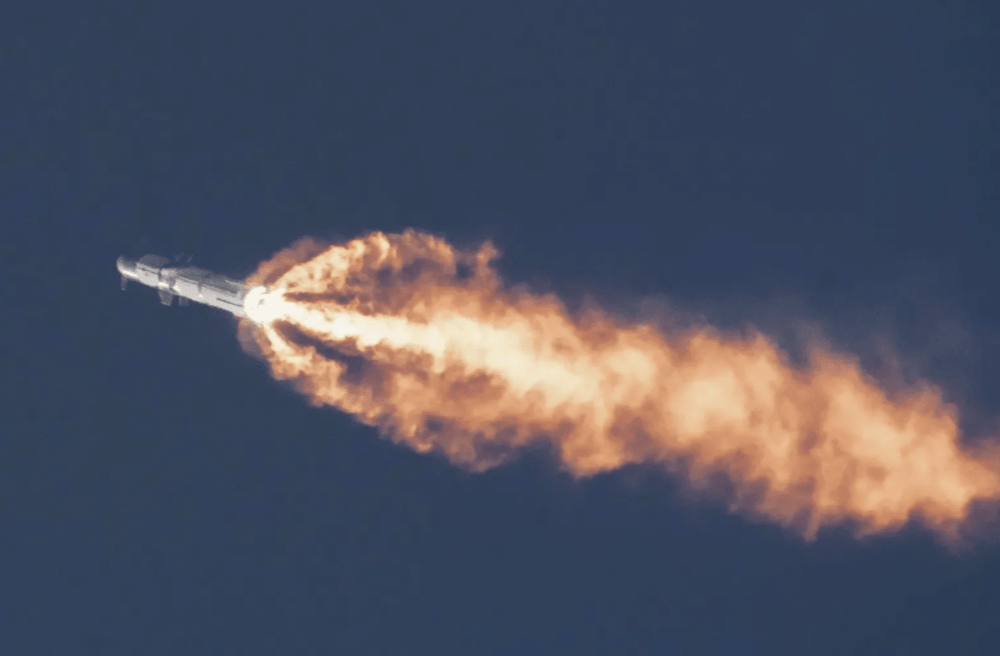
Despite a dramatic and largely successful liftoff, the Starship lost stability approximately midway through its planned trajectory, scattering debris over the Caribbean and forcing regional air traffic rerouting. While not categorized as a total failure, the flight missed critical performance benchmarks, including controlled reentry and orbital data transmission.
SpaceX has acknowledged the vehicle experienced "unplanned disassembly," a euphemism for catastrophic failure. While partial progress was made in terms of altitude and separation staging, the core objectives—orbital velocity and payload simulation—remained unachieved. This setback adds to growing concerns about the maturity of the Starship system, which is central not only to SpaceX’s Mars plans but also to NASA’s Artemis lunar program and multiple U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) contracts.

Key Facts
Vehicle: Starship, 400 feet tall, tallest and most powerful rocket ever built.
Launch Site: SpaceX Starbase, Boca Chica, Texas.
Event: Loss of flight control mid-mission; vehicle disintegrated over the Caribbean.
Outcome: Did not meet orbital velocity or payload simulation goals.
Aviation Impact: Dozens of commercial flights rerouted due to debris risk.
Mission Status: Partial success with major engineering failures.
Strategic Importance: Vehicle tied to NASA Artemis program and future DoD missions.
Funding: Privately backed, USD-denominated contracts with U.S. federal agencies.
Investor Sentiment and Regulatory Concerns
The failed test triggered muted but noticeable ripples in financial and aerospace circles. While SpaceX is privately held and does not trade on public indices like SPX, the broader aerospace and defense sector showed sensitivity to the incident, particularly among suppliers and satellite operators relying on Starship’s future viability.
Industry analysts note that while rapid iteration is a known hallmark of SpaceX’s engineering philosophy, repeated high-profile failures could lead to tighter scrutiny from the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and delay timelines for the Starship’s operational deployment. Elon Musk, CEO of SpaceX and Tesla $TSLA, maintained his typical posture on social media, emphasizing “data-rich failure” over stagnation.
NASA, a key stakeholder with plans to use Starship as a lunar lander, has thus far withheld criticism, reiterating its support for commercial innovation. However, delays in readiness could impact the timeline of the Artemis program, which is already under pressure due to budget constraints and technical risks.

Key Takeaways
Mission exceeded previous altitude records but failed to complete orbital objectives.
Loss of vehicle mid-flight underscores unresolved stability issues in Starship’s design.
Airspace disruptions illustrate rising regulatory challenges as test scope grows.
NASA and DoD programs may face knock-on delays due to reliability concerns.
SpaceX’s rapid-prototype culture remains controversial in aerospace risk management circles.
Starship’s Future Hinges on Technical Maturity and Regulatory Trust
Tuesday’s test was a partial success at best and a stark reminder of the technical complexity behind deep space launch systems. While SpaceX continues to iterate at breakneck speed, the mission exposed vulnerabilities that could slow the path to Mars and impact national security payload timelines.
The broader implications stretch beyond just one company. As the U.S. doubles down on space infrastructure in both civilian and defense spheres, the reliability of private launch partners becomes a systemic concern. For SpaceX, balancing innovation with regulatory compliance and mission assurance will be vital in maintaining stakeholder trust and achieving its long-term vision.














Comments